Observations of An Effective Hybrid Focus Group Facilitation

Author: Ada Tai, MBA, CPHR, SHRM-SCP
Conducting focus groups is nothing new for people who work in management, research, human resources and other areas. A focus group is a moderated session that gathers a small group of people to discuss specific topics. Recently, our firm was retained to facilitate a series of focus group sessions with diverse businesses on a complex issue. Our senior team member, Bob Excellent, renowned in stakeholder engagement and facilitation, was assigned as the facilitator. Opportunities like this do not happen every day. Our team members treated this as a professional development opportunity. Therefore, we took turns assisting Bob at these sessions so we could observe and learn from him.
To make focus groups successful, thoughtful preparations are needed!
Pre-Focus Group Preparation:
| 1. We worked closely with the regional authority who engaged us to understand the background of the situation, the expected deliverables and the targeted audience. | ||
| 2. Based on adult engagement principles and given the tight schedules, we designed five sessions, each for 60 minutes, with the option of having individual chats afterwards. | ||
| 3. To encourage participation: | ||
| a. We secured a location that is easily accessible and with ample parking spots. | ||
| b. We capped each session at 7 participants. A hybrid option was offered to those who could not participate in person. | ||
| c. On the focus group invitation: | ||
| i. We outlined the objectives and the major questions we would discuss. To complete every session in 60 minutes, we created 5 main questions. | ||
| ii. We also explained how the facilitator would maintain confidentiality. | ||
| iii. Snacks and coffee always go a long way. We included a message about these “incentives.” | ||
| iv. We promoted an interactive atmosphere but declared that reservation is a must. | ||
| 4. Within our team, roles were also assigned: | ||
| a. Bob, the Facilitator, would plan and chair the session, and address inquiries. | ||
| b. Another team member, the Supporter, would manage the logistics, such as space rental, emergency protocols, snacks arrangement, technology set up and note taking. | ||
| c. Both people would set up the room together before the session started. | ||
During the session:
Bob is an early bird: he is the first person to arrive on all occasions. No surprise, he was 40 minutes earlier for each focus group session.
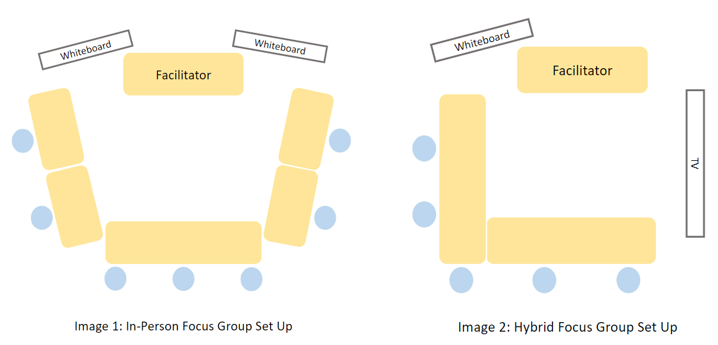
For sessions with no virtual participants, the room was arranged in an open-ended “U-Shape” configuration as in Image 1. On the day I was the Supporter, we had two virtual participants. Therefore, we set up the room as in Image 2. I observed Bob putting the participant’s first name on the name card and putting each card at the table to hint at the seat allocation. He also wrote down our names and roles on the whiteboard in the room.
When participants entered the room, he stood up to shake hands and greet each person, asking their names and taking them to their designated seats. He also greeted and waved to each online participant.
Bob kicked off the session on time by briefly presenting himself and introducing the session. He then highlighted the concept of confidentiality and certain ground rules. The rules include the following:
- All perspectives/feedback are welcomed.
- People need to demonstrate respectful behaviour towards each other.
- Due to the limited time, participants will be cut off if they dominate a conversation.
- Attendees may leave early or take a call, but they should keep their phone mute.
The participants were given 30 seconds to introduce themselves and their businesses. The virtual participants were also reminded that they could connect with the room via chat or speak through their microphone. They were asked to have their camera on. As the Supporter, I managed the chat box throughout the session.
Bob planned how much time he wanted to spend on each question. He did not announce each question by saying, “Now, let’s discuss the first question, which is xxx.” Instead, he led people through a conversational flow. Throughout the hour, Bob balanced the “talkers” and the “quieters.” He also aligned and re-aligned the group with the objectives of the session. Additionally, he closely observed people’s body language and encouraged participation by calling them by their first name. Bob probed on several answers and used the participants’ comments to lead into the next part of the discussion. Occasionally, a person would not have anything to contribute to the question, but Bob made that person feel at ease.
The session finished in exactly one hour! Bob officially ended the session by thanking everyone for their input. He acknowledged that due to the time constraints, there was no “group hug”; however, it was critical to hear from diverse perspectives. He sensed that several people had more to say.He put our business cards on the table for those interested. The virtual attendees can receive our business cards via email. Then he offered casual chats for those wanting to stay and discuss further, including virtual attendees. The attendees told us that not only they shared their opinion, but the session also opened their eyes to other perspectives on the issue.
After the session:
After everyone left, Bob and I debriefed the session and reviewed notes to ensure we captured the discussions. We also reflected on what, if anything, needed to be adjusted for future sessions.
Conducting an effective (hybrid) focus group requires thoughtful planning, diligent preparation and professional conversation control. Since most focus groups are open-ended and opinion-based, a skilled facilitator is needed to balance hearing people out and managing the required outcomes.
BadaB Consulting Inc. provides a wide range of human resources solutions, including Strategic HR and Succession Planning, Organizational Design & Development, Merger & Acquisition Support, Recruitment, Skills Development Training, Compensation Design, Performance Management, Workplace Investigation, Policy Development, etc. Another specialty of BadaB’s services is personal job search and career coaching. The team has effectively helped over 500 people to find work.
Contact information:
- Website: www.badab101.com
- Blogs: https://www.badab101.com/blog
- LinkedIn: BadaB-Consulting-Inc
- Facebook: @badabconsulting
- YouTube: BadaB Consulting Inc.
The views and opinions expressed in this blog post belong solely to the original author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views and opinions of CPHR Alberta.
The views and opinions expressed in this blog post belong solely to the original author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views and opinions of CPHR Alberta.