
CPHR Canada's Updated Competency Framework: What Changed and How it Affects Members
27
Jul 2023
526

Author:
Erica Blain, Director, Professional Standards, Registrar, CPHR Alberta
In late 2021, CPHR Canada announced the introduction of an updated Competency Framework for the HR profession. Many members have reached out with questions on what was updated, why and how it affects them on the path to the designation or in mainiting their designation. The CPHR Alberta Professional Standards team, has put together this blog to answer some of the most frequently asked questions!
How was it updated and why?
In many ways, the competency framework has remained much the same but with some key changes to ensure that the CPHR designation remains relevant and topical in today’s changing world. Human Resources is a field that has grown, expanded and diversified over many years since it’s inception as a profession. CPHR Canada worked closely with HR professionals across Canada to amend the framework so that it is in-line with the working world today and in the near future.
The updated Competency Framework recognizes that there is no longer an ideal role, position or way of functioning for the HR Professional, instead, providing a strategic approach that matches the pace of change. Human Resources has such a broad scope and it is becoming more valued in organizations every day. By updating the Competency Framework, we are keeping up with the growth and progression of the profession as a whole and trying to incorporate all professionals within the field.
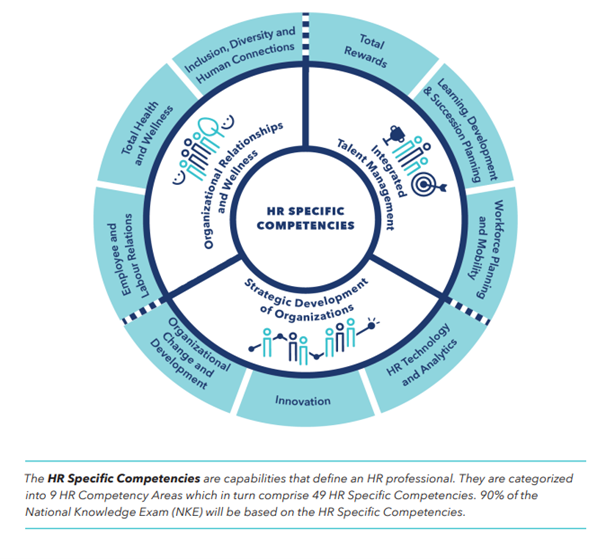
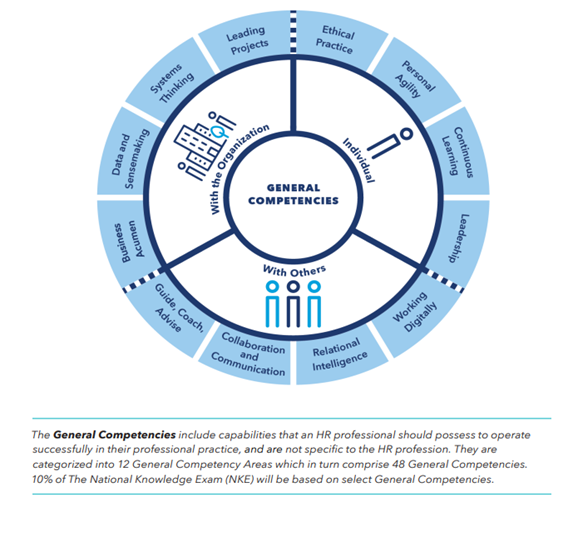
What has changed?
While the changes to the Competency Framework were not sweeping, you will see some smaller amendments. One update is the introduction of the competency entitled Innovation. Especially through the pandemic, HR professionals were forced to be agile and innovative to continue to do their roles but in a changing environment and continuous legislation or safety protocol updates. The demand on HR to innovate and be adaptable has become more vital than ever and is an important area of focus.
Additionally, you’ll see what used to be just “engagement” is now Inclusion, Diversity and Human Connection. Again, in the past few years we have seen an increased call for employers to ensure an inclusive environment is provided to all employees. Also, diversity is an active goal for many organizations and is better recognized, appreciated, and celebrated. CPHR Canada wanted to ensure that these important concepts were incorporated into the Competency Framework because they are so valued by employees and employers alike.
Another change was to remove the competency area Professional Practice. This competency focused on legislation and ethics, having business acumen and leadership skills. These skills are now incorporated within the newly introduced General Competencies instead.
In the previous Competency Framework, there were enabling competencies which incorporated a diverse set of skills into five loosely related areas. With the new framework, the scope has been broadened but also refined into twelve non-HR competencies, which are termed General Competencies.
The overall result of these changes led to the establishment of HR Competencies that are more specific to the work of today’s HR professional. The separation of competencies into HR-Specific Competencies and General Competencies helps the field move beyond the silos of “functional” HR areas, which results in the structure of the new framework being more strategic and integrative. These enhancements showcase the greater breadth of the practice of HR and reflect how the evolution of the professional is playing out in workplaces across Canada.
How do the changes affect members?
For members looking to write the National Knowledge Exam, the exam is based upon this updated Competency Framework. The General Competencies are covered lightly on the exam, making up just 10% of the questions. The other nine competencies are each covered with 10% of the exam.
The framework is also the foundation for those going through the Experience Validation Assessment. Candidates for the CPHR designation will need to show that they have proficiency in a variety of competencies in order to be successful on the experience assessment and gain the CPHR designation.
For members who already have their CPHR designation, this only affects them as they complete their Continuing Professional Development (CPD) requirements. In order for activities to count towards the CPD requirement, the activities need to be linked to at least one area of the Competency Framework. Because the framework is extensive and clear, it is quite simple for Chartered Members to ensure their CPD requirements fall into these categories.
The framework really covers everything HR so using the framework as a foundation for further learning or education is a great way to better yourself professionally. If you are looking for ways to expand your knowledge or if you want insight into which areas you require further information or training, looking at the competencies is a great starting point as it outlines what HR professionals should know in order to be the best they can be for their employees and organization as a whole.
The views and opinions expressed in this blog post belong solely to the original author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views and opinions of CPHR Alberta.

We’re excited to congratulate the CPHR Alberta 2025’s scholarship recipients! Each year, these awards help us recognize emerging HR talent and support students who are taking meaningful steps toward their future in the profession. CPHR Alberta scholarships play an important role in easing financial barriers, celebrating academic achievement, and connecting students with the professional community that will support them as they work toward earning the CPHR designation. Below, meet this year’s outstanding recipients. CPHR Alberta’s Eldon Emerson Scholarship: Undergraduate Award Created in 2021, the Eldon Emerson Scholarship honours Eldon’s exceptional leadership, contribution, and passion for the HR profession. Eldon received the Fellowship Award in 2013—one of the highest honours in our community, recognizing exemplary service and impact. 2025 Eldon Emerson Award Winner Chine Rajafa CPHR Alberta’s Diploma Scholarship: Undergraduate Award Launched in 2023, the Diploma Scholarship supports student members enrolled in a 2‑year HR diploma program. Recipients show strong academic performance, community involvement, and a clear commitment to the HR profession and the CPHR designation pathway. 2025 Diploma Scholarship Award Winner Mehar Kaur Follow Their Journey We encourage you to connect with Chinenye and Mehar on LinkedIn and support them as they begin their HR careers. A simple follow, message, or connection can go a long way for emerging professionals. Watch for 2026 Scholarship Dates The next intake period for CPHR Alberta’s Scholarship Program opens Fall 2026. Follow us on LinkedIn and Instagram for updates. Become a Student Member Whether you're studying in an accredited HR program or building your skills through part‑time, continuing education, or bridging programs, CPHR Alberta has a student membership option designed to support your path into the profession. Joining as a student member gives you access to resources, events, and a community that can help you take your next step with confidence. Learn more and join

Plan your 2026 professional development in advance and discover what CPHR Alberta has planned for you! Below is a brief overview of the programming coming your way in the months ahead. For full details, visit our new PD Calendar , and check your Member Portal regularly for updates. Signature Events Member Recognition Gala – April 30, 2026 | The Westin Airport Hotel, Calgary We invite you to an evening of celebration, connection, and inspiration. The Member Recognition Gala is a formal event honouring the individuals, teams, and projects shaping the future of HR across Alberta, the Northwest Territories, and Nunavut. Inspired by the Aurora Borealis, this redesigned experience replaces traditional awards with Spotlights—a meaningful way to recognize excellence in action. Tickets will go on sale soon. CPHR Alberta 2026 Conference: Future-Ready HR – June 2–3, 2026 | BMO Centre, Calgary Our 2026 Conference prepares human resources (HR) professionals to master the fundamentals, embrace innovation, and build executive-level influence—creating agile organizations ready for economic and workforce change. A future-ready HR community. Registration will be opening soon. Chapter Community Events | Throughout 2026 We’ll be visiting all chapters across the year with popular community events in your region. Stay tuned for event announcements and details. Stampede Breakfast | July | Calgary, AB A member favourite breakfast event is returning! Join us to mingle, connect, and enjoy the energy of Stampede. More information will be shared soon. Certificates Workplace Investigations Training | February 17–19 and March 17–19 Presented in partnership with Veritas Solutions. The Workplace Investigations Certificate is a three‑day program focusing on three core training topics. Participants may register for the full program or select stand‑alone courses. A certificate is awarded upon completion, and no prerequisites are required. Webinars Networking at Noon Join us for one hour each month to explore current and emerging HR topics. With a new focus every session, you'll leave with thought‑provoking questions and earn 1 CPD hour. On February 12, join us for HR Trends & Priorities for 2026. International Women’s Day National Event Join us on March 4 from 10:00–11:30 a.m. for a special fireside chat with Layne the Auctionista and Sheena Russell, founder of Made with Local . This national celebration of International Women’s Day explores the theme “Give to Gain,” highlighting how generosity and purpose‑driven leadership can shape meaningful careers. You’ll hear real stories, bold insights, and practical inspiration you can take back to your HR practice. Details ®gistration: https://cphrns.ca/events/EventDetails.aspx?id=2018615&group= Virtual Sessions for Students Students can expect two sessions each month: one dedicated to building skills one offering practical advice from HR professionals in the field These sessions are complimentary for Student Members. Are you interested in becoming a member? Students receive complimentary membership. Learn more: www.cphrab.ca/student-programs Other Events DisruptHR YYC 13.0 will take place in October. More details will be shared in late summer. Plan Your Year With Us Explore the full list of programs and events on our 2026 PD Calendar.
In 2025, CPHR Alberta became a partner to the Collaborative Funders Table and the Calgary Youth Employment Initiative to address under-employment for opportunity youth. Over seven months, more than 60 partners came together to research, design, and test what would become OY Works . That story of co-creation is what makes this toolkit different. Employers shared what they need to know and what tools would make a difference. CPHR Alberta members contributed HR expertise through representation on the steering committee, and participation in surveys, interviews, and protype testing throughout 2025. Attracting, engaging, and retaining young talent isn’t just a workforce strategy — it’s an investment in our collective future. When we empower youth with meaningful opportunities, modern skills, and a sense of belonging, we build workplaces that are more innovative today and more resilient tomorrow. The organizations that thrive will be the ones that recognize youth not as the workforce of the future, but as essential contributors shaping the world right now. A dedicated toolkit to hire opportunity youth gives HR professionals and employers the practical resources, insights, and frameworks they need to connect with young people authentically — turning intention into action and helping break down barriers and supporting organizations to build strong, sustainable talent pipelines. Co‑designed with HR professionals and industry leaders, the toolkit reflects real challenges and real solutions, ensuring it is both practical and deeply aligned with the needs of today’s evolving workforce. - Lisa Watson, CPHR Alberta Board Director, OY Works Steering Committee Member Today marks an exciting milestone: the launch of OY Works , an online toolkit designed to make inclusive youth hiring easier for Alberta employers and HR professionals. This free resource was co-created by a diverse group of stakeholders—employers, HR experts, and non-profit agencies—who share a common goal: opening doors for young people who are ready to work but face barriers. Why OY Works? Too many youth are eager to contribute, learn, and grow, yet struggle to access meaningful employment. OY Works is here to change that. Built with practicality and purpose in mind, the toolkit offers actionable strategies to help businesses recruit, onboard, and retain Opportunity Youth—young people aged 18–29 who are not currently in school, training, or work. What’s Inside the Toolkit? It makes business sense: Read the Business Case for hiring Opportunity Youth and be empowered to influence leaders. Explore the ideas and tools in the Quick Start Hiring Guide . Learn how to onboard effectively and build retention from day one in the Optimal Onboarding & Mentoring Guide and the Retain & Grow Guide . Discover how non-profit agencies are preparing OY for the workplace. They often support employers and employees through all stages of employment. This isn’t just about doing good—it’s about making smart business decisions. Inclusive hiring strengthens workplace culture, reduces turnover, and taps into a motivated talent pool ready to make a difference. We invite you to explore OY Works and join the movement to create opportunities for youth who deserve a chance to shine. Explore the OY Works toolkit: https://bit.ly/3L6SQuF When young people get a chance to contribute, it’s a win for youth, employers and the community. Join us in spreading the word by sharing the toolkit with your networks.


