Pink Shirt Day – The Connection to Bullying in the Workplace

Author: Rob Dombowsky, MBA, CPHR – Lethbridge, Alberta Chapter Committee
Many people look back on their childhood in fond memory of their time at school with their classmates and friends. Unfortunately, many people do not have the same fond memories because they were victims of bullying and harassment. They were singled out for this behaviour for many reasons, which could include their race, ethnicity, sexual orientation, disability or family. Many people were also picked on for any perceived minor social infraction such as belonging to a certain clique, such as the skaters, geeks, metalheads or because a boy wore a pink shirt or a girl wore a boy’s shirt. In truth, kids could use any excuse they could justify.
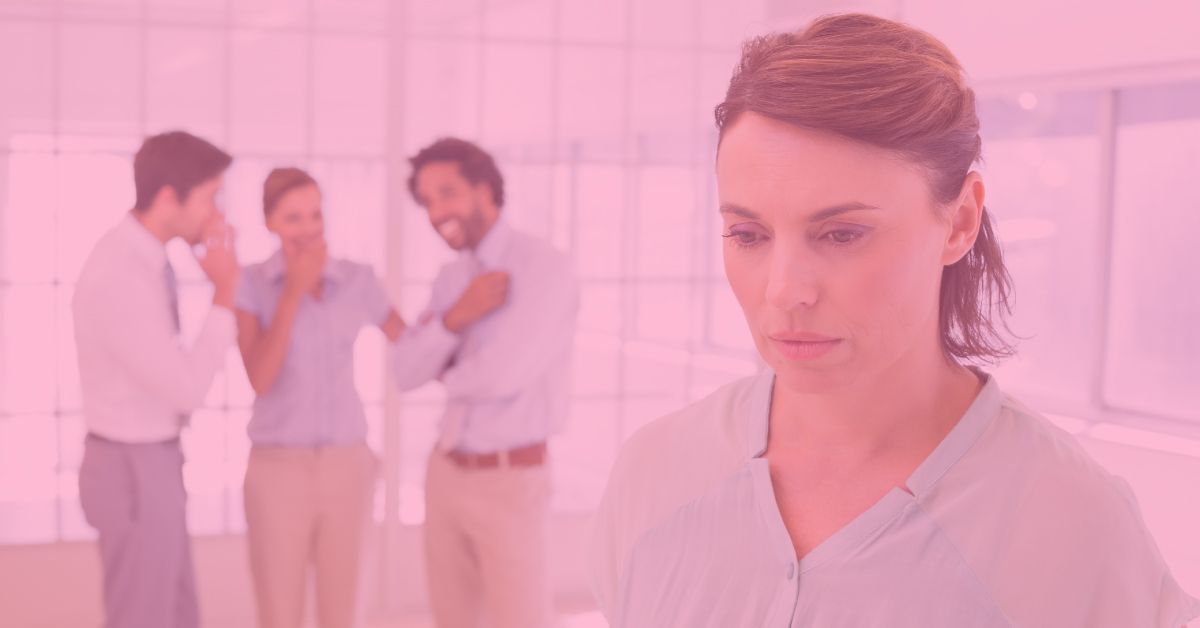
Unfortunately, as we grew up, graduated, entered the workforce, some of those bullies came with us. Most people undergo a period of growth or maturation. By the end of young adulthood, most people have matured enough and understand social norms of behaviour. Others though carry on the behaviour for several reasons such as feelings of inadequacy, insecurity, powerlessness and a subsequent need to control others. [1] It can be described as a type of paranoia in which the bully misreads hostility in neutral situations. [2] That said, there are many reasons for being a bully and there is no age limit.
Bullies can also be male or female, and the behaviour of either gender can be equally damaging to the victims. Male bullies are more likely to engage in overt acts of aggression, such as verbal abuse, taking something or violence. Females are less likely to engage in overt acts and bully by manipulating or damaging relationships, such as starting a false and hurtful rumour, excluding people or giving the silent treatment amongst other negative behaviours. [3]
This type of behaviour became such an issue in workplaces, that governments decided to intervene. The OHS Act definition of harassment is paraphrased as an incident of objectionable or unwanted conduct, comment, bullying or action taken by a person that they should reasonably know it could cause offence or humiliation or affect health and safety. [4] Which includes physical as well as psychological health and safety. This is a very broad definition and includes bullying, discrimination, violence and sexual solicitation.
The OHS Act also requires employers to ensure, as reasonably as practicable, that workers are not subjected to or participate in harassment or violence in the workplace. [5] Supervisors are required to ensure that their workers are not subjected to harassment or violence. [6] Workers are also required by the act to not participate in acts of bullying or harassment. [7] Similar obligations exist at the federal level and can be found in the Canada Labour Code.
Employers should be aware of the direct and indirect costs that bullying and harassment can have on their organizations. Several employers have been taken to the Human Rights Commission, others have had claims for psychological injuries resulting from bullying and harassment accepted by WCB. Other employers simply had to defend themselves in civil court against such charges. No matter the outcome, there is a real financial cost to employers.
I would argue, that bullying and harassment are learned behaviours. Kids learn it from their friends, classmates or family. I don’t believe that a child is born a bully. In watching my kids at a young age, I see only the best of humanity. As they aged, they made mistakes and their friends and family would correct the behaviour. In my experience, I think friends and peers have a lot of influence over a young person, and perhaps more than some parents. I have seen kids standing up and saying loudly, that this type of behaviour is not OK. I have also seen others learn from that and support their peers.
On Feb 23, 2022, the world will celebrate Pink Shirt Day. Pink Shirt Day resulted from two Canadian junior high students protesting the bullying of a young boy by classmates for wearing a pink shirt to school. They bought 50 pinks shirts from a discount store, texted their friends about the plan, went to school the next day, and handed out the shirts. By the end of the day, 200 students were protesting the behaviour by proudly supporting their bullied classmate by wearing pink. Today, pink shirt day is celebrated around the world. [8]
I know for one, my family will be proudly supporting pink shirt day. If we as a society can teach children respect, one day those children will become our employees and employers. How different will the workplace be then?
References
[1] Kirby, S.,The Top Reasons Why People Bully (June 16, 2021), Betterhelp.com, https://www.betterhelp.com/advice/self-esteem/the-top-reasons-why-people-bully/
[2] Bullying. (Retrieved 1 February 2022). Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/ca/basics/bullying
[3] Bullying. (Retrieved 1 February 2022). Psychology Today. https://www.psychologytoday.com/ca/basics/bullying
[4] Occupational Health and Safety Act, Statutes of Alberta, 2020 Chapter O-2.2 (1 December 2021) Section 1(n), https://www.qp.alberta.ca/1266.cfm?page=O02P2.cfm&leg_type=Acts&isbncln=9780779826728
[5] Occupational Health and Safety Act, Statutes of Alberta, 2020 Chapter O-2.2 (1 December 2021) Section 3(1)(c), https://www.qp.alberta.ca/1266.cfm?page=O02P2.cfm&leg_type=Acts&isbncln=9780779826728
[6] Occupational Health and Safety Act, Statutes of Alberta, 2020 Chapter O-2.2 (1 December 2021) Section 4(a)(iii), https://www.qp.alberta.ca/1266.cfm?page=O02P2.cfm&leg_type=Acts&isbncln=9780779826728
[7] Occupational Health and Safety Act, Statutes of Alberta, 2020 Chapter O-2.2 (1 December 2021) Section 5(1)(d), https://www.qp.alberta.ca/1266.cfm?page=O02P2.cfm&leg_type=Acts&isbncln=9780779826728
[8] Our Mission. (Retrieved 4 January 2022). Pink Shirt Day. https://www.pinkshirtday.ca/about
The views and opinions expressed in this blog post belong solely to the original author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views and opinions of CPHR Alberta.
The views and opinions expressed in this blog post belong solely to the original author(s) and do not necessarily represent the views and opinions of CPHR Alberta.